GRC
Since ancient times, the concept of governance, risk management, and compliance (GRC) has been integrally woven into the notion of how a corporation should be operated. As technologies and the size of the market grew, the need to have GRC as a tool increased, in the wake of multiple disasters that rocked the foundation of the world as we knew it.
GRC evolved into a marketable utility that allows companies to digitally manage their business processes. There was less data to be concerned about because practitioners could only see a portion of their business at once thanks to modular tools.

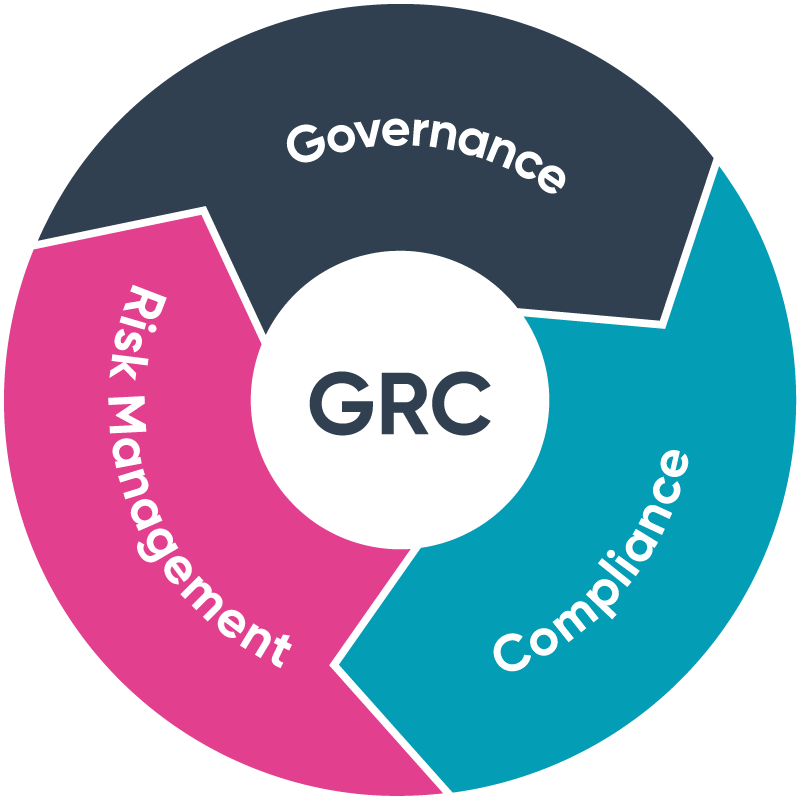
GOVERNANCE, RISK MANAGEMENT & COMPLIANCE:
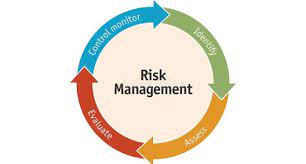
Risk Management

Compliance
GRC ADVANTAGES

Stability
By establishing GRC, risk exposure, both short-term and long-term, is resolved, allowing for an adaptable and scalable control environment.
Optimization
To save time and avoid any undesired variations, non-value-adding operations are eliminated and value-adding activities are streamlined. Automated detective controls, which improve efficiency and traceability, should be used instead of manual preventative measures.

Transparency
GRC makes it possible to see a more full picture of the organisation and processes, giving owners access to and control over the information they need to comprehend the profile of their business units and any relevant risks and difficulties.

Reduced Costs
Lower costs play a part in the overall ROI advantages that efficient GRC activities represent. Maintaining redundant controls, tests, problems, solutions, and reporting across several disciplines also results in lower maintenance costs.
Reduced Costs
Lower costs play a part in the overall ROI advantages that efficient GRC activities represent. Maintaining redundant controls, tests, problems, solutions, and reporting across several disciplines also results in lower maintenance costs.
WHAT MAKES GRC SO EFFICIENT AND RELIABLE?
- Secure Architecture
- Audit-Ready Reporting
- Pre built Security Practices
- Supports Custom Security Policies
- Public & Private Business Deployment

WHAT MAKES GRC SO EFFICIENT AND RELIABLE?
- Secure Architecture
- Audit-Ready Reporting
- Pre built Security Practices
- Supports Custom Security Policies
- Public & Private Business Deployment

IMPLEMENTING GRC IN YOUR ORGANIZATION:
-
The GRC Capability Model’s four components are as follows:
- LEARN about the context, culture, and important stakeholders of the organisation in order to inform objectives, strategy, and actions. In order to develop meaningful goals, you must learn about the major impacting elements in both your internal and external company environments throughout this step.
- ALIGN strategy with objectives and actions using effective decision-making that takes into account values, opportunities, threats, and requirements, with strategy.
- PERFORM in ways that encourage and reward positive behaviours, stop and correct negative behaviours, and quickly identify when something happens.
- REVIEW the strategy and actions’ operational efficacy and design, as well as the continued suitability of the organization’s improvement goals.


THE EASE/BENEFITS OF GRC
- Stakeholders depend on strong business results and expect organizations to operate with high levels of transparency. GRC can help in fulfilling this.
- The regulatory environment is volatile and uncertain and GRC helps in overcoming this obstacle.
- Risk management now poses significant challenges due to the third-party relationship industry’s exponential growth. Third parties can expose your company to liability for their ethical/compliance failings in addition to being a risk if they do not provide their service or product on schedule.
- The costs of addressing risks and regulatory requirements are spiraling out of control and GRC capabilities can help organizations navigate and thrive in today’s challenging and complex business environment.
- There are harsh consequences when threats and opportunities aren’t identified. Using GRC these threats are eliminated.

GRC TOOLS
- Pathlock
- Fusion Framework System
- Riskonnect
- IBM OpenPages
- LogicManager
- StandardFusion
- MetricStream
- SAI360

QUERY
frequently asked questions
- Software Tools that are designed to integrate the Corporate Governance activity in line with everyday business processes facilitating GRC Management , with access to complete logs, reports and analysis of the Regulatory Processes.