Application Security CHALLENGES
Protection of sensitive data: Application Security helps protect, store and process sensitive information such as personal data, financial information and confidential business information.
Preventing malicious attacks: Applications Security often help mitigate cyberattacks, such as hacking, viruses, and malware which can cause data breaches and financial loss.
Maintaining trust: Secure applications help maintain trust with users, customers, and stakeholders.
Compliance with regulations: Best Application Security Strategies help companies comply with industry regulations that require the protection of sensitive information, such as the EU’s General Data Protection(GDPR) and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
Start your Application Security journey with the right tools to secure development, pre-production security testing, & production environment.

MITIGATE SECURITY RISK WITH RIGHT AAPLICATION SECURITY

It is significant that developers know about the most well-known application security chances ones that typically result from unstable code so they can check the bases they need to cover at each phase of the development pipeline.
Identify components with known vulnerabilities in Application Security.
Protect against Data leaks and exposure with Application Security.
Identify Weak backend access controls with Application Security.
Prevent Injection Attacks with Application Security.
Fix Broken authentication and authorization with Application Security.
Achieve BUSINESS GOALS BY APPLICATION SECURITY
Applications are a vital piece of working together in our current reality where everything interfaces with the web or mobile apps. The Internet of Things, hyperconnectivity, and client requests necessitate that organizations use application security to provide ease of use for consumers and employees, and they make a difference in competitive markets.
Application Security have help Businesses achieve its Goals by :
Reduce Risk — Including those from third-parties
Protect Brand Image — by projecting security and preventing leaks
Protect and Build Customer Confidence — Customer experience is driving competition
Protect and Safeguard Data — both your own and your customers
Improve Trust from customers, investors, and lenders — Mitigating risk improves trust from all parties

application security to devsecops
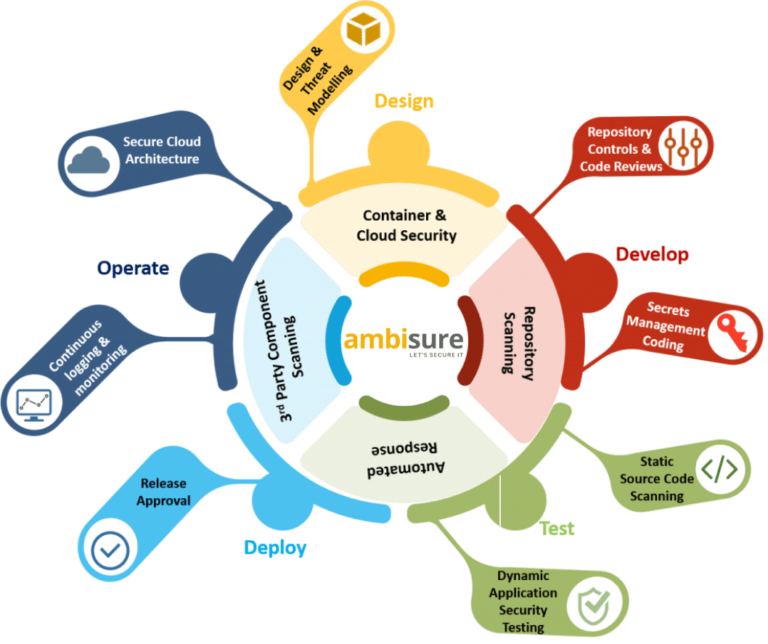
- DevSecOps, or secure DevOps, is the outlook in programming development that everybody is answerable for app security.
- DevSecOps is the integration of security practices into the software development and operations processes to secure applications and infrastructure.
- DevSecOps helps to prevent security vulnerabilities from being introduced and to catch & remediate them quickly.
- By integrating security into the DevOps process, organizations can improve the overall security of their applications and reduce the time and effort required to fix security issues.
- The goal of application security and DevSecOps is to incorporate security affirmations into development cycles and custom line of business (LOB) applications.
Application security testing Solutions
SOLUTIONS
Website Security Solutions are
QUERY
frequently asked questions
- Application security is the most common way of creating, adding, and testing security highlights inside applications to forestall security vulnerabilities against dangers like unapproved access and data breaches.
- Today’s applications are often available over various networks and connected to the cloud, increasing vulnerabilities to security threats and breaches.
- IAST (interactive application security testing) analyzes code for security vulnerabilities while the app is run by an automated test, human tester, or any activity “interacting” with the application functionality. This technology reports vulnerabilities in real-time
- A security audit is a systematic evaluation of the security of a company's application by measuring how well it conforms to an established set of criteria.
Managing application security risk has become increasingly complex as more enterprises rely on third-party applications when deploying or building software. Tracking risk in internal DevSecOps is one thing, but managing risk from software acquired elsewhere is quite another.
- Cross-site scripting
- Out-of-bounds write
- Improper input validation
- Out-of-bounds read
- Improper restriction of operations within the bounds of a memory buffer
- SQL injection
- Exposure of sensitive information to an unauthorized actor
- Use after free
- Cross-site request forgery (CSRF)
- OS command injection